When the hackers get hacked

Blog
When the hackers get hacked:
a blog series unveiling the Conti ransomware family
Or read part 2: dissecting the attack
On 24 February 2022, Russia declared war on Ukraine and started its invasion. Subsequently, many ransomware gangs and other hacking groups started announcing with whom their allegiances lie [1].
After expressing their explicit support on 25 February 2022 for the Russian government and threatening to "strike back at an enemy's critical infrastructure", the group operating the Conti ransomware family has faced severe backlash. Not only from cyber security professionals worldwide but also anti-Russian members within their own organisation [2] [3] [4]. A Ukrainian security researcher [5] under the alias ContiLeaks [6] took up digital arms and started leaking internal chats, source files, screenshots, manuals and other files. We will report on these leaks in a series of blog posts to come. Our goal is to understand better how the ransomware gang operates, who is involved and when, what challenges they face, and how are they organised. As we proceed with our research, we will report on interesting, noteworthy and critical findings from the leaks. To kick off the blog post series, we describe Conti, present an overview of the typical organisation of ransomware groups internally and present the data that has been leaked so far.
Who is Conti?
The Conti ransomware family was first seen in August 2020 and is allegedly operated by the Wizard Spider group [7] [8]. The Wizard Spider group consists of approximately 80 members and is based in and around St Petersburg in Russia. The group has been extorting companies in western countries using ransomware since at least 2017. First, the group extorted victims using Hermes ransomware between February 2017 and 2018. Then, the group switched to Ryuk ransomware between 2018 and 2020 [9] [10]. Subsequently, the group switched over to Conti ransomware and has been attacking companies using that ransomware until now. In the recent leaks, it is apparent that the group allegedly has received over $2,700,000,000 in BTC between April of 2017 and February 2022 [11]. This money likely originates from ransom payments made by victims of the group.How are ransomware gangs organized?
Northwave created a framework on what roles there are inside a ransomware gang based on key insights from dealing with ransomware incidents. As part of our incident response process, we investigate the root cause of such incidents and talk to the actors behind the ransomware attack. From our experiences, we deducted that there are currently seven distinct roles within a ransomware attack. Each role follows from the objective of the attack's specific activities. We would see each of these roles fulfilled by the same actor in the past. However, in recent years, we have seen that more and more actors are specialising in a single role within this model.
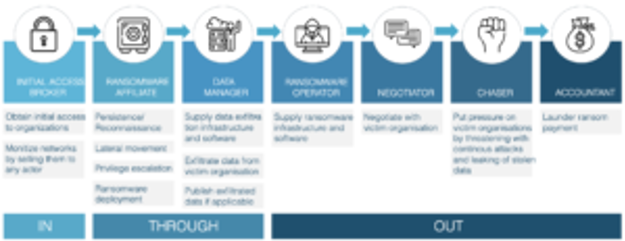
As part of a blog series called Inside the world of ransomware, we wrote a more detailed overview of the different roles within a ransomware attack [12]. We will investigate if the roles identified by Northwave are also identifiable in the leaked documents and describe how the different actors interact.
Leaked data
The first leak took place on 27 February. In the days following, more data has leaked. As it stands, the current number of leaked files is 39. Below we constructed an overview of all the leaked files and a short description of what the leak contains.| Original file name | Description |
| 1.tgz | Jabber chat logs 2021-2022 |
| 2.tgz | Jabber chat logs 2020 |
| Screenshot from 2021-12-15 21-26-28.png | Chat with victims |
| Screenshot from 2021-12-06 22-57-52.png | Chat with victims |
| bazar_bots_domains_html.7z | Bazar panel |
| bazar_bots_comments_html.7z | Bazar panel |
| Screenshot from 2021-12-06 22-58-32.png | Chat interface |
| Screenshot from 2021-12-15 17-29-58.png | Cobalt Strike interface |
| Screenshot from 2021-12-15 17-31-08.png | Cobalt Strike interface |
| Screenshot from 2021-12-15 21-26-28.png | Chat with victims |
| conti_locker_v2.zip | Encrypted archive with source code |
| bazar_bots.7z | Bazar panel |
| backdoor.js.zip | .git folder with js and c++ refs |
| sendmail-master-0a343a19f4f48dd8efd6c052c092fd5feec916ad.zip | Source code |
| backdoor-master-3ad175864899c85021fa04cb24848a2bc66b1d16.zip | Source code |
| import-master-ac16d180c391fce7a644f6c2a30fc3cfb37451f6.zip | Source code |
| cadmin-master-b2675af7f27c05513f1fd8374ee7bc35a058f18f.zip | Source code |
| admin-master-deb4694b0e9110ffcf84a42f70874a6e152c0b32.zip | Source code |
| spoked-master-cf530950c30b81188d40c56b9a66e7d3bb21710c.zip | Source code |
| storage_ebay_checker-master-599bede833e26b11db10fce55ee08ddd15280a6b.zip | Checks ebay account balance for given username and password |
| srw-master-df4b6eddf7fdd2e07fb75d0492deeeb2e15f959e.zip | Laravel application |
| storage_go-master-f4617f09d47a978d1128e0e1d77259900d62aac1.zip | go files that parse IPs and store them in a local postgres database |
| storage_ex-master-e4827b099abefd719fc674519ea0d2622ea304e0.zip | Source code |
| storage-master-3607d1f6a72e28efe84b55e8a660ff97db0e79a2.zip | Source code |
| 185.25.51.173-20220226.json | Jabber chat log 26-02-2022 |
| 185.25.51.173-20220227.json | Jabber chat log 27-02-2022 |
| 185.25.51.173-20220228.json | Jabber chat log 28-02-2022 |
| FMvM2_PXsAMdOof.png | Conti storage server |
| FMvNB1mWUA4l4ud.png | Screenshot with networking configs |
| FMvNWvqWYAEZ298.png | Screenshot with networking/wireshark configs |
| rocket-chat.tgz | Rocket chats 2020-2022 |
| trickconti-forum.7z | Manuals/how-to's |
| 3.tgz | Binman/docs repo |
| FMwnZodWYAE1vDX.png | Screenshot of jabber chat with privnotes |
| trickbot-command-dispatcher-backend.tgz | Erlang source code of application |
| trickbot-data-collector-backend.tgz | Erlang source code of application |
| FMw3KrXXEAUXAQJ.png | Sergei Loguntsov (https://github.com/loguntsov) aka. begemot |
| conti_locker.7z | Conti source without locker src. |
| jabber_logs.7z | Jabber chat logs 1st and 2nd of March 2022 |
We will add any additional leaks to this list. The list was updated last on 2-3-2022 at 22:00 UTC. So far, the leaks seem only to contain internal communication of the Conti group. Northwave did not identify any data of her clients yet in the leaks. Of course, Northwave will closely monitor this and update any of her clients if their data becomes apparent in the leaks.

